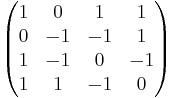Conference matrix
In mathematics, a conference matrix (also called a C-matrix) is a square matrix C with 0 on the diagonal and +1 and −1 off the diagonal, such that CTC is a multiple of the identity matrix I. Thus, if the matrix has order n, CTC = (n−1)I. Some authors use a more general definition, which requires there to be a single 0 in each row and column but not necessarily on the diagonal.[1][2]
Conference matrices first arose in connection with a problem in telephony.[3] They were first described by Vitold Belevitch who also gave them their name. Belevitch was interested in constructing ideal telephone conference networks from ideal transformers and discovered that such networks were represented by conference matrices, hence the name.[4] Other applications are in statistics,[5] and another is in elliptic geometry.[6]
For n > 1, there are two kinds of conference matrix. Let us normalize C by, first (if the more general definition is used), rearranging the rows so that all the zeros are on the diagonal, and then negating any row or column whose first entry is negative. (These operations do not change whether a matrix is a conference matrix.) Thus, a normalized conference matrix has all 1's in its first row and column, except for a 0 in the top left corner, and is 0 on the diagonal. Let S be the matrix that remains when the first row and column of C are removed. Then either n is evenly even (a multiple of 4), and S is antisymmetric (as is the normalized C if its first row is negated), or n is oddly even (congruent to 2 modulo 4) and S is symmetric (as is the normalized C).
Contents |
Symmetric conference matrices
If C is a symmetric conference matrix of order n > 1, then not only must n be congruent to 2 (mod 4) but also n − 1 must be a sum of two square integers;[7] there is a clever proof by elementary matrix theory in van Lint and Seidel.[6] n will always be the sum of two squares if n − 1 is a prime power.[8]
Given a symmetric conference matrix, the matrix S can be viewed as the Seidel adjacency matrix of a graph. The graph has n − 1 vertices, corresponding to the rows and columns of S, and two vertices are adjacent if the corresponding entry in S is negative. This graph is strongly regular of the type called (after the matrix) a conference graph.
The existence of conference matrices of orders n allowed by the above restrictions is known only for some values of n. For instance, if n = q + 1 where q is a prime power congruent to 1 (mod 4), then the Paley graphs provide examples of symmetric conference matrices of order n, by taking S to be the Seidel matrix of the Paley graph. The first few possible orders of a symmetric conference matrix are n = 2, 6, 10, 14, 18, (not 22, since 21 is not a sum of two squares), 26, 30, (not 34 since 33 is not a sum of two squares), 38, 42, 46, 50, 54, (not 58), 62 (sequence A000952 in OEIS); for every one of these, it is known that a symmetric conference matrix of that order exists. Order 66 seems to be an open problem.
Example
The essentially unique conference matrix of order 6 is given by
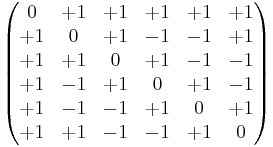 ,
,
all other conference matrices of order 6 are obtained from this one by flipping the signs of some row and/or column (and by taking permutations of rows and/or columns, according to the definition in use).
Antisymmetric conference matrices
Antisymmetric conference matrices can also be produced by the Paley construction. Let q be a prime power with residue 3 (mod 4). Then there is a Paley digraph of order q which leads to an antisymmetric conference matrix of order n = q + 1. The matrix is obtained by taking for S the q × q matrix that has a +1 in position (i,j) and −1 in position (j,i) if there is an arc of the digraph from i to j, and zero diagonal. Then C constructed as above from S, but with the first row all negative, is an antisymmetric conference matrix.
This construction solves only a small part of the problem of deciding for which evenly even numbers n there exist antisymmetric conference matrices of order n.
Generalizations
Sometimes a conference matrix of order n is just defined as a weighting matrix of the form W(n, n−1), where W(n,w) is said to be of weight w>0 and order n if it is a square matrix of size n with entries from {−1, 0, +1} satisfying W Wt = w I.[2] Using this definition, the zero element is no more required to be on the diagonal, but it is easy to see that still there must be exactly one zero element in each row and column. For example, the matrix
would satisfy this relaxed definition, but not the more strict one requiring the zero elements to be on the diagonal.
Telephone conference circuits
Belevitch obtained complete solutions for conference matrices for all values of n up to 38 and provided circuits for some of the smaller matrices. An ideal conference network is one where the loss of signal is entirely due to the signal being split between multiple conference subscriber ports. That is, there are no dissipation losses within the network. The network must contain ideal transformers only and no resistances. An n-port ideal conference network exists if and only if there exists a conference matrix of order n. For instance, a 3-port conference network can be constructed with the well-known hybrid transformer circuit used for 2-wire to 4-wire conversion in telephone handsets and line repeaters. However, there in no order 3 conference matrix and this circuit does not produce an ideal conference network. A resistance is needed for matching which dissipates signal, or else signal is lost through mismatch.[9]
|
As mentioned above, a necessary condition for a conference matrix to exist is that n−1 must be the sum of two squares. Where there is more than one possible sum of two squares for n−1 there will exist multiple essentially different solutions for the corresponding conference network. This situation occurs at n of 26 and 66. The networks are particularly simple when n−1 is a perfect square (n = 2, 10, 26, …).[10]
Notes
- ^ Malcolm Greig, Harri Haanpää, and Petteri Kaski, Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A, vol. 113, no. 4, 2006, pp 703-711, doi:10.1016/j.jcta.2005.05.005
- ^ a b Harald Gropp, More on orbital matrices, Electronic Notes in Discrete Mathematics, vol. 17, 2004, pp 179-183, doi:10.1016/j.endm.2004.03.036
- ^ Belevitch, pp. 231-244.
- ^ Colbourn and Dinitz, (2007), p.19
van Lint and Wilson, (2001), p.98
Stinson, (2004), p.200 - ^ Raghavarao, D. (1959). "Some optimum weighing designs". Annals of Mathematical Statistics 30 (2): 295–303. doi:10.1214/aoms/1177706253. MR0104322. http://projecteuclid.org/euclid.aoms/1177706253.
- ^ a b van Lint, J.H., and Seidel, J.J. (1966), Equilateral point sets in elliptic geometry. Indagationes Mathematicae, vol. 28, pp. 335-348.
- ^ Belevitch, p.240
- ^ Stinson, p.78
- ^ Belevitch, pp.240-242
- ^ Belevitch, p.242
References
- Belevitch, V. (1950), Theorem of 2n-terminal networks with application to conference telephony. Electr. Commun., vol. 26, pp. 231–244.
- Goethals, J.M., and Seidel, J.J. (1967), Orthogonal matrices with zero diagonal. Canadian Journal of Mathematics, vol. 19, pp. 1001–1010.
- Seidel, J.J. (1991), ed. D.G. Corneil and R. Mathon, Geometry and Combinatorics: Selected Works of J.J. Seidel. Boston: Academic Press. Several of the articles are related to conference matrices and their graphs.
- Colbourn, Charles J.; Dinitz, Jeffrey H. (2007) Handbook of Combinatorial Designs, Boca Raton, Florida: Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, ISBN 1584885068.
- van Lint, Jacobus Hendricus; Wilson, Richard Michael (2001) A Course in Combinatorics, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0521006015.
- Stinson, Douglas Robert (2004) Combinatorial Designs: Constructions and Analysis, New York: Springer, ISBN 0387954872.